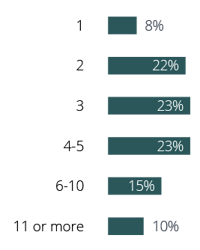Return on investment (ROI) is a core KPI that determines the profitability of an investment. Measuring SEO ROI helps you track progress, measure SEO profitability, make data-driven decisions, and grow your business by increasing your SEO budget.
But where do you start and how do you measure the ROI of SEO campaigns?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is SEO ROI?
SEO ROI (return on investment) refers to the business value derived from SEO activities in comparison to the costs incurred.
It measures the return on SEO investment for a single campaign and overall SEO strategy.
The purpose of calculating ROI in SEO is to analyze SEO’s performance in detail. It lets us make better decisions based on the effectiveness of different SEO campaigns.
When you run multiple SEO campaigns across your sales funnel, you need to know which tactics have the highest ROI (so you can continue to increase their budget) and which ones failed to perform (so you can take corrective action via experimentation).
This leads to improved SEO performance as you can channelise your SEO budget.
SEO ROI improves your ability to make right, data-driven SEO and marketing decisions because it eliminates gut feeling and judgement.
What SEO Metrics Should You Measure?
You need to use a metric that is relevant to your business’s sales goals. All other SEO metrics are secondary.
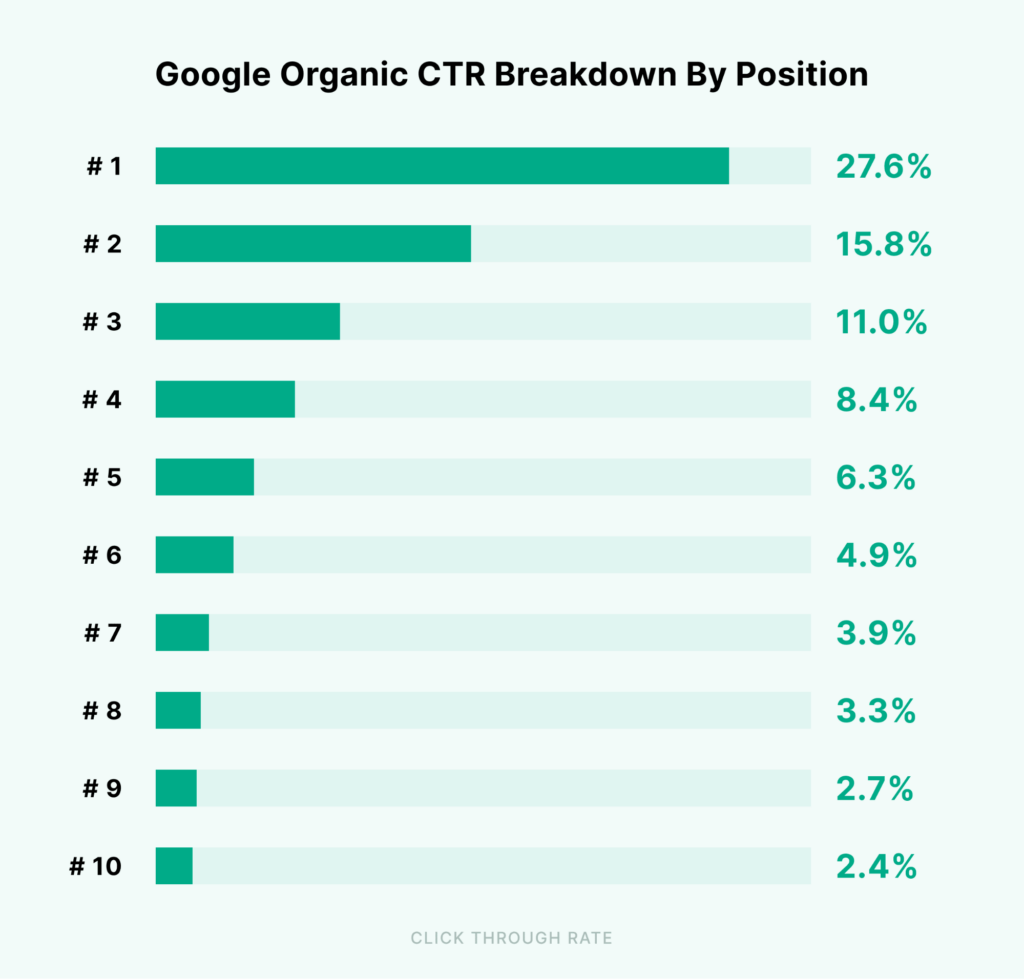
For example, organic traffic is the main SEO metric for ROI. But, more organic traffic doesn’t mean a high conversion rate and more sales.
For SEO ROI, the best metric is one that’s directly linked to revenue. These metrics can be sales in the case of an ecommerce store and qualified leads for B2B businesses (unless you have sales tracking enabled for your B2B business).
Here’s a list of the essential SEO metrics to measure return:
- Organic traffic: It tracks the visitors you receive from search engines.
- Conversions: Not all organic visitors convert and it makes sense to track organic conversions to measure SEO performance. It refers to calculating the conversion rate of the traffic you receive from search engines.
- Sales: Not all conversions are sales. Tracking sales generated via SEO is one of the most reliable metrics.
- Revenue: Attributing revenue to SEO campaigns makes it easy to track SEO ROI. But, revenue attribution isn’t as simple as it seems. Customer touchpoints can spread across many marketing channels (paid search, social media, email marketing etc).
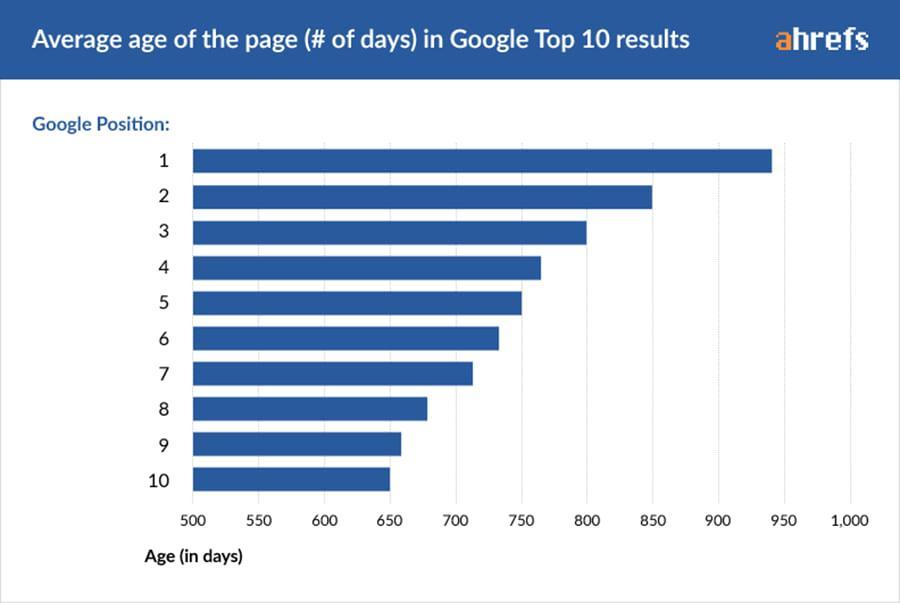
- Keyword ranking: It refers to tracking the keyword position of your target keywords in SERPs. When keyword ranking improves, it indicates your SEO efforts are successful.
- Domain rating: Domain or page-related authority or rating determines the SEO strength of the domain or page. High domain authority improves the ranking of all the internal pages by passing authority to internal pages.
- Backlinks: Number of new backlinks acquired in a certain time.
How to Measure SEO ROI?
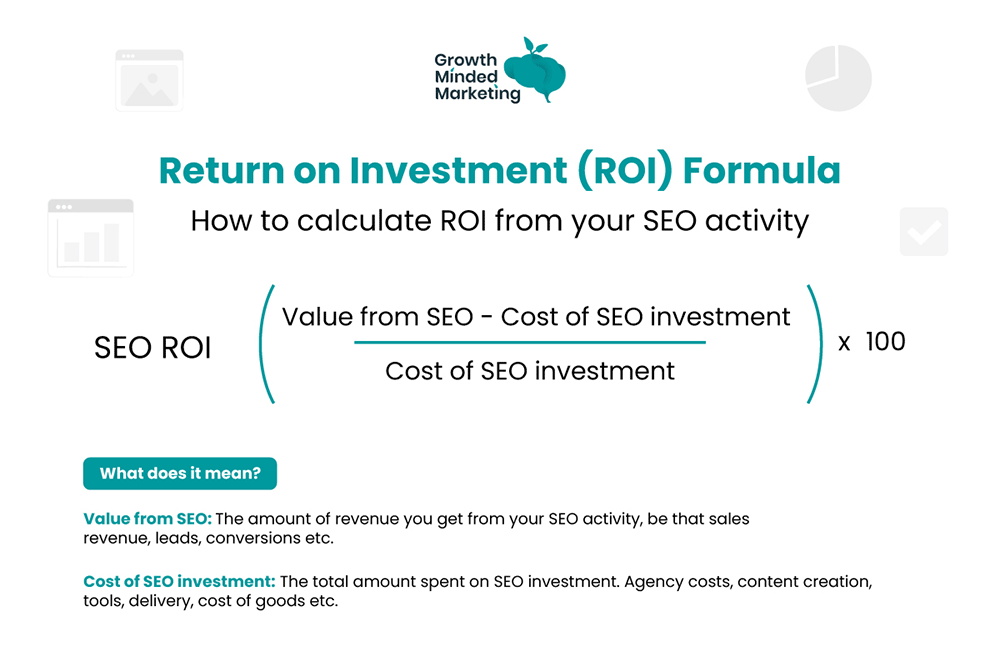
The formula to track SEO ROI is:
SEO ROI = (Value from SEO – Cost of SEO investment) / Cost of SEO investment x 100
The resulting number is a percentage that shows how much you make from SEO when you spend a fixed amount.
You can calculate ROI for individual SEO campaigns, tactics, and entire strategy.
You need to find two variables to calculate SEO ROI:
- Cost of SEO investment
- SEO value generated through the investment.
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow.
1. Cost of SEO investment
The first step in ROI calculation for SEO is to track the cost of SEO investments. This includes tracking and measuring the end-to-end cost of running an SEO campaign.
SEO costs may include:
- Freelancer or SEO agency cost
- In-house costs including salaries and administration
- Website maintenance, tools and app cost.
It’s important to identify the right SEO campaign and calculate its cost specifically for accurate ROI calculation.
Let’s take an example.
You decided to publish 8 blog posts per month for 6 months to triple your site’s organic traffic. You hired an SEO agency to create, publish, and distribute content. The agency charged you £8,000 per month for 8 posts. The total cost of the SEO campaign turned out to be £48,000.
If you choose to create content in-house, you’ll account for employee salaries, SEO tools, and miscellaneous costs.
It requires proper account maintenance to accurately identify and distribute costs across different SEO and marketing campaigns that run simultaneously.
2. SEO value
How much SEO value your has investment generated in a specific period?
This is the hard part as measuring SEO value and attributing it to the correct source isn’t a straightforward task.
You can use multiple tools to track and attribute SEO value to the right campaign. These include:
- Google Analytics to attribute traffic, conversions, and sales to the right touchpoint (see more details here)
- Search Console
- Behavioural analytics tools like heatmaps and session recording apps
- SEO tools like Semrush and Ahrefs
- Email marketing platform to track conversions
- CRM tool to identify leads and sales.
Measuring the true SEO value is easy for some businesses like ecommerce stores where they can create an attribution model in Google Analytics and figure out what percentage of sales are generated by organic traffic.
B2B businesses in service industries can find it harder to accurately calculate the SEO value generated by a specific campaign.
They usually have a lengthy sales cycle which requires multiple touches which makes attributing sales complicated.
A study reported that the majority of B2B businesses need between 2 and 5 touches to generate a qualified lead:
Your broad SEO goal also plays a major role in how you calculate SEO value.
Campaigns aimed at increasing organic traffic, keyword ranking, or domain rating are easy to track as you can use tools to measure performance.
In these cases, you need to quantify SEO value (as ROI can’t be calculated if SEO value is a qualitative variable).
For example, an increase in domain rating from 25 to 30 needs to be converted into monetary SEO value. This is often hard and can’t be done accurately as it requires judgement.
Similarly, when your SEO goal is tripling organic traffic in 6 months, you need to generate a monetary value for organic traffic to measure SEO ROI.
On the flip side, SEO campaigns focused on generating conversions, sales, or revenue are hard to track as you require proper tracking and attribution modelling to credit the right touchpoint for a conversion or sale.
It gives you a monetary value for your SEO campaigns which makes it easy to calculate SEO ROI accurately.
Calculate SEO ROI
Once you have the cost of SEO and SEO value in quantifiable, monetary form, you can find ROI with the following formula:
SEO ROI = (Value from SEO – Cost of SEO investment) / Cost of SEO investment x 100
So, if you invested £48,000 on 48 blog posts over six months which resulted in sales worth £61,000 (hypothetically), here’s how you’ll measure ROI:
SEO ROI = (61,000 – 48,000) / 48,000 = 0.270
Since ROI is represented in percentages, converting 0.270 into a percentage:
SEO ROI = 0.270 x 100/100 = 27%
So in our example, it means that every £100 spent on SEO activity for this campaign resulted in £127.
Further Reading
6 Tips to Ensure You’re Measuring the Right SEO Metrics
Dealing with SEO cost and value gets much easier and the journey to measuring SEO ROI becomes smooth when you are tracking the right metrics.
The following best practices will help you identify and track the right metrics to calculate ROI for SEO:
1. Use objectives to find the right metric
The goal of your SEO campaign or strategy defines what metric you should use to measure ROI.
If your SEO goal is to generate 200 organic sales per month, organic conversion rate is the right metric.
If your SEO objective is to reach the number one position in Google and Bing SERPs for a target keyword, ranking is the right metric for your campaign.
You can solve this metric dilemma during the goal-setting stage. When you define an SEO objective, ask yourself how you’ll measure the success and ROI.
It’ll help you identify a goal with a relevant SEO metric that’ll make things easier.
If you don’t have a metric to track SEO performance and calculate SEO ROI, it’ll become a nightmare to fix things when a campaign ends.
2. Avoid tracking too many metrics
Selecting the most appropriate SEO metrics and ignoring all the other less important metrics is important. Otheyou might end up tracking data that doesn’t make any sense.
How many metrics you have to track to accurately measure SEO ROI depends on your business model and industry.
Ecommerce stores can track sales and revenue generated by SEO in Google Analytics for ROI measurement.
A B2B business on the other hand, would need to track multiple metrics for revenue attribution.
Generally, you need to track the most important metrics and leave all the others.
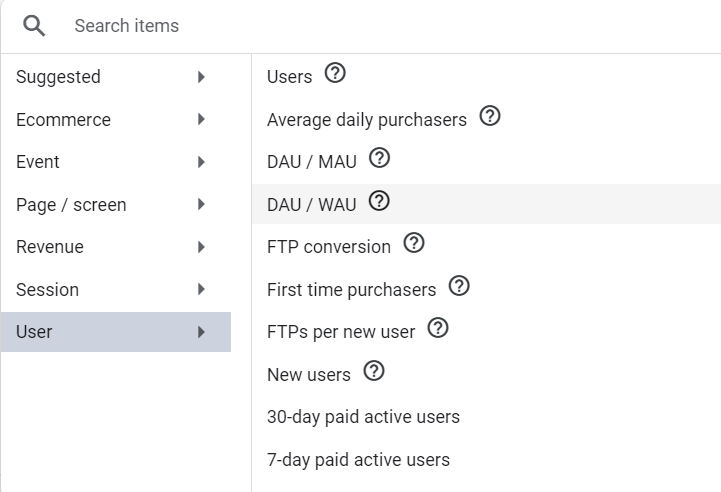
There are several metrics in Google Analytics to track organic users including users, total users, new users, returning users, sessions, average engagement time per session, first visit, page view, and several others:
It’s tempting to analyse all these metrics to better understand your target audience, but do you need all of these for SEO ROI?
No.
You need to choose the metrics that are most relevant to your SEO campaign and its goal to accurately measure ROI.
Sure, you can analyse and use this data in any way you like for your business, but you need only a few metrics (such as the revenue generated, conversions, or leads captured turned into paying clients) to measure the performance and ROI of your campaign.
3. Track correct data
Multiple SEO metrics with minimal differences lead to another issue of tracking incorrect data.
There isn’t any simple (or even hard) way to differentiate between correct and incorrect data. You’ll always get ROI for SEO when you add numbers to the formula.
Incorrect data leads to inaccurate ROI which has dire consequences for your business.
Correct data means:
- Using the right metric to track SEO performance
- Using data from the correct investment and return period
- Measuring SEO cost accurately including all the minor and major costs
- Data cleaning before it’s used for calculation
- Identifying the right SEO value that is generated by the same SEO campaign
- Attribution modelling
- Converting qualitative into quantitative variables accurately for reporting and ROI calculation.
4. Use the right time period
It’s hard to accurately measure the true SEO value generated by a campaign because it’s extremely difficult to identify the exact return period.
For example, a blog post published today has potentially no fixed return period as it’ll continue to generate SEO value indefinitely.
One study reported that it takes an average of 2+ years to reach Google’s first page:
Once you reach those top positions, that’s when your content will start getting the lion’s share of organic traffic:
SEO generally, an exponential effect that grows over time and this makes it extremely hard to pinpoint the exact return duration of your SEO efforts.
What you can do is identify a fixed period per investment based on historical data of your site to track correct data for ROI measurement.
For example, if analytics shows that a single post has an upward traffic trend for up to 15 months across your site, you can use it to identify an average return time.
5. Don’t ignore context
It’s important to consider the perspective and context when measuring ROI for SEO.
SEO performance and cost are impacted by multiple factors that are beyond your control such as spikes in demand, seasonality, and recent trends.
For example, seasonal content drives more organic traffic in some months and you might not see any traffic in the off-season.
You need to understand the context and variable factors when measuring SEO value. If you aren’t seeing positive results now, figure out the reason.
Is it a seasonal trend or did the SEO campaign fail miserably?
Also remember that SEO performance is linked with the performance of other marketing channels.
For example, if you are running a social PPC campaign on Meta to boost brand awareness, you might see a corresponding increase in organic impressions of branded keywords.
These linkages and perspectives must be given due consideration when measuring SEO ROI.
6. Quantify the metric
As discussed already, it’s essential to convert SEO metrics into quantifiable variables for ease of measurement and tracking.
Most of the core SEO metrics are quantitative and can be translated into meaningful SEO value. Some aren’t, such as keyword ranking and domain authority.
It’s hard to measure SEO value for certain metrics, and it’s hard to track their impact on SEO performance. Consequently, measuring ROI gets challenging.
Domain authority is one such metric. You can create an SEO campaign to increase the domain authority of your website from 50 to 60 in 12 months.
…But it’s hard to measure SEO value driven by this increase as it’ll impact your entire domain and internal pages.
Determining the actual value of an SEO campaign helps solve this problem.
How much SEO and non-SEO value does your business expect to receive after an increase of domain authority from 50 to 60?
Convert it into a monetary value and you’ll be able to track your ROI.
Do this for all the qualitative metrics for accurate measurement of SEO ROI.
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow.
Conclusion
SEO ROI, despite all its limitations, is a must-have. The concept that SEO traffic is ‘free’ is flawed.
It isn’t free.
When it’s not free, you have to measure its ROI to figure out how profitable it is and whether you should invest more in it.
Start measuring the return on investment of your SEO campaigns today using the techniques and tips discussed above.
If it seems challenging, you can reach out to us and book a strategy call.
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow in 2024