If your business has an international presence and you target people from different countries who speak different languages, you can leverage international SEO for exponential growth and reach.
…and no, having a website in English with a .COM TLD doesn’t mean your website is ready and optimised for international traffic.
You might get traffic from different regions, but you are missing a lot of potential buyers who speak other languages in your primary markets.
Table of Contents
ToggleLet’s explore what international SEO is, how to get started, and best practices.
What is international SEO?
International SEO refers to the process of optimising your website for an international audience.
You can drive traffic from different parts of the world to your website and divert visitors to relevant landing pages and local versions of your site.
International SEO focuses on two major aspects:
- Multi-regional SEO
- Multilingual SEO.
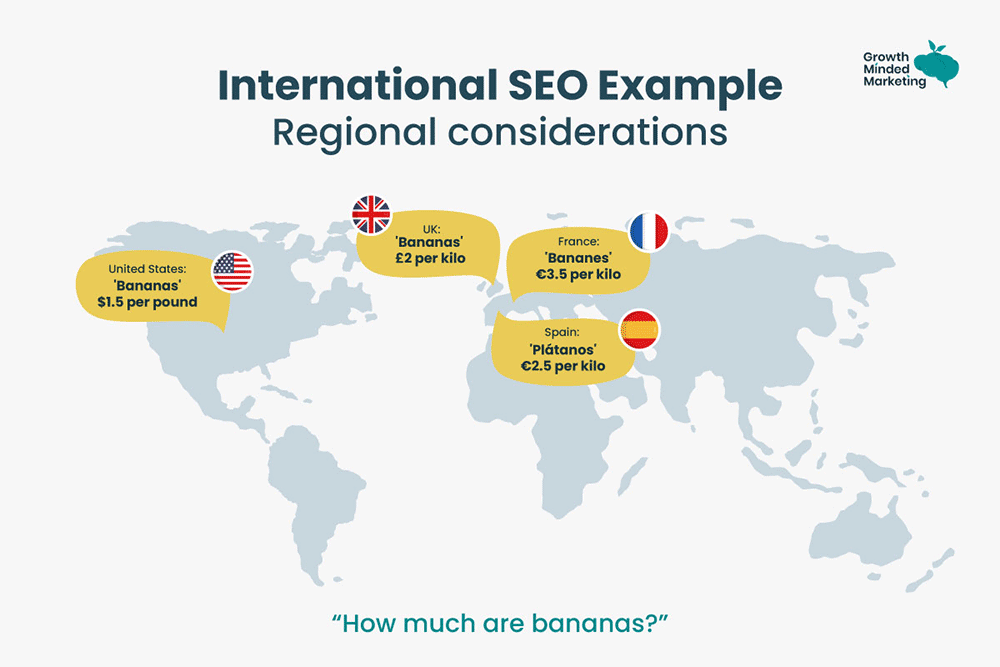
Here’s an example of how international SEO works:
Imagine you sell t-shirts in the US, Canada, UK, Australia, and Singapore. You have to create a country-level website to send traffic to the relevant website. You’ll have to optimise content locally to rank for keywords such as ‘t-shirts in Singapore’ and ‘buy t-shirts in Australia’.
You don’t necessarily have to change the language for these 5 countries as English seems to work but content, pricing, and offers would need to be optimised, this market level optimisation process is what we call international SEO.
International SEO is also pivotal for targeting localised search queries as in the absence of this it would be difficult to get your site ranking.
Why You Need Dedicated Landing Pages for International SEO
One of the basic rules of international optimisation is to create highly personalised landing pages for each target market. If you are targeting, say 25 countries, you may need to create at least 25 versions of your website with landing pages (one per market).
Doing so has multiple benefits:
Better search engine rankings
Google and other search engines work as local search engines. Someone in Australia searching for “t-shirts” will always see local stores and sites (irrespective of their domain name). Google might not serve any non-local website (no matter how authoritative it is).
Secondly, as more people access the internet from their phones (up to 96.5%), almost all searches are now local as Google tracks location and serves local websites and businesses.
This makes it essential to have dedicated landing pages as part of your international SEO strategy as it helps improve search ranking across regions and markets.
You can target local keywords and acquire backlinks from region-specific domains to send the right signals to search crawlers.
Improved targeting
Dedicated landing pages are targeted leading to a better UX. You can incorporate geographical marketing tactics to boost conversion rates.
For example, you can launch a custom-made t-shirt based on a popular phrase from a series that is being aired in a country. This phrase might be alien to people living somewhere. These types of customised experiments and targeting options are unlocked when you have one website per market.
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow.
Relevant content
You can create relevant content with high accuracy for different buyer personas and submarkets within each market. You can connect at a personal and emotional level with your audience through content that addresses their unique needs. This can be achieved with different versions of your site.
Local offers and prices
It gets easier to show prices in local currencies with dedicated pages designed for different locations. It helps you manage and calculate taxes, shipping costs, duties, and other expenses.
Offers can also be tweaked based on where your ideal customer is located. For example, if it’s the rainy season in a country, apparel stores can push and highlight relevant seasonal clothing to boost sales.
Subdomain vs. subfolder: What to choose for international SEO?
The big question is how to create dedicated versions of your site for international search optimisation. The two most common options include:
- Subdomain
- Subfolder.
Let’s discuss the pros and cons of both.
1. Subdomain
A subdomain is a part of the main domain and acts as a separate, distinct website. Here’s an example of a subdomain:
Using subdomains for international SEO is a less popular method as search engines consider each subdomain almost as a different website.
This means each subdomain will need separate crawling and indexing. The link equity from the main domain doesn’t pass as effectively to subdomains as it does to subfolders.
Having said that, subdomains offer some key benefits. You can fully customise each subdomain and treat it as a separate website.
You can also host your subdomains on local hosts which improves speed and helps somewhat in local SEO.
Pros:
- Customisable and controllable
- Easy management.
Cons:
- Lower link value
- Requires separate crawling at the subdomain level
- High maintenance cost.
2. Subfolder
It refers to a folder that is located within the root domain. Here’s an example of a domain subfolder:
Subfolder or subdirectory is the most popular approach to international SEO. It is affordable and straightforward as everything sits within a single domain. You can easily create dedicated landing pages for different locations.
Subdirectories lack customisation, this tends to get trickier when using a CMS with limiting capabilities like WordPress, meaning you’ll have to use the same template for all markets which tends to restrict creativity and functionality.
Pros:
- Cost-effect and easy management
- Domain authority is passed to inner folders which improves ranking
- Minimal maintenance
- Simple reporting
Cons:
- Lacks customisation and flexibility
- SEO can get challenging for big websites as you have to ensure crawlers treat subdirectories as local versions.
Further Reading
7 International SEO Best Practices
Here’s a list of the best practices to optimise your site for an international audience:
1. Define international markets
Selecting the international markets you want to target and then clearly defining the scope and SEO goals for each market is the most essential part of international SEO.
The primary question you need to ask yourself is: Do we need to enter a new market?
Not all markets are worth targeting… and you can’t just target a country for the sake of international SEO or going global.
Ultimately the decision should be based company goals and what the regional research shows.
So, how do you select the right markets?
You need to find gaps and growth potential.
Three proven ways to find target markets are:
- Check and analyse analytics and search data. Find out the top countries based on traffic
- Analyse competitors using a tool like Semrush and check country-wise traffic. Is there a location you aren’t targeting but your competitors are getting massive traffic?
- Use location-based keyword research to find high-potential international keywords that are relevant to your niche.
You need to prioritise international markets based on certain variables such as business preference, ease of ranking, growth potential, local competition, etc.
Ideally, you should start with one international market at a time.
This will help you implement international SEO with full focus. It is also more cost-effective to enter one market than several at a time so if you are on a tight budget, choose the location that has the highest potential to rank.
2. Keyword research
International SEO requires that you do keyword research for every location. All the leading keyword research tools provide country-specific keyword data and that’s what you need to use.
For example, ‘apple pie recipe’ has 148K search volume in the US with 55 KD, according to Ahrefs. (read more about keyword density and why it matters in keyword research in this guide):
The same keyword has a 15K search volume in Canada with 65 KD which means it’s much harder to rank in Canada for the ‘apple pie recipe’ keyword:
You also need to consider terminologies that vary across countries that speak the same language.
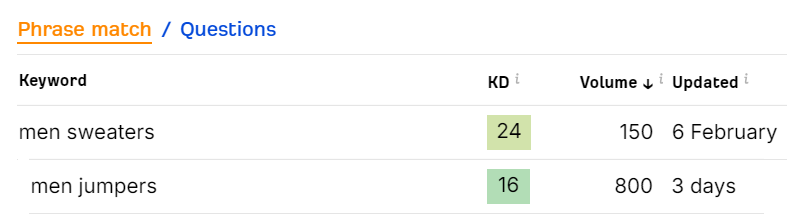
For instance, the jumper is a common word used for sweaters in the UK while the sweater is commonly used in the US.
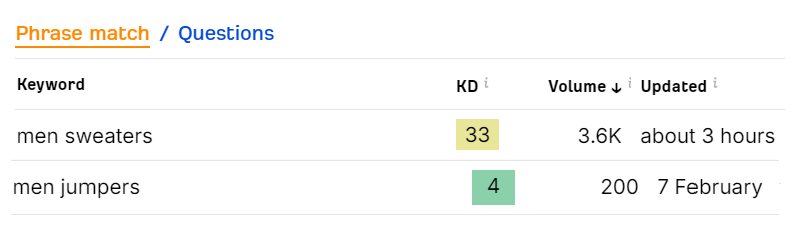
Men jumpers has a high search volume in the UK while men sweaters have a low volume:
Here’s how the two keywords look like in the US:
These types of differences in terminologies have a bigger impact on search intent than keyword volume.
In the US, a ‘jumper’ doesn’t mean a sweater – rather it is used for a pullover.
Other factors that impact keyword research, search intent, and targeting are:
- Change in spelling such as color vs colour
- Cultural differences
- Norms and traditions.
Using the same set of keywords in another country isn’t a good idea even if they both have the same native language (e.g – English or Spanish).
You need to conduct keyword research from scratch considering all the variables for every new market (ideally one at a time).
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow.
3. Add hreflang accurately
Hreflang is a language meta tag for search engines to show them alternative URLs for different languages your content is available in.
Here’s an example of hreflang:
link rel=”alternate” href=”http://example.com” hreflang=”es”/>
The tag tells search engines to show relevant language to the visitors based on their location so you don’t have to IP redirect visitors. In the above example, a person visiting your site from a Spanish-speaking country will be served the Spanish content instead of English.
It directs visitors to the right version based on their location leading to better UX. Implementing hreflang is essential for international search engine optimisation.
You can refer to this page to find the correct language code and use this free tool to create hreflang tags. You might also need to target countries that speak a specific language and this can be done using this list of country and regional codes.
For example, if you want to show the Portuguese version of your site to visitors from Brazil, you’d use br with the language code like this:
link rel=”alternate” href=”https://example.com/br/” hreflang=”pt-br” />
There are 3 ways to implement hreflang tag:
- Add in the HTML head of your page
- HTTP headers
- Sitemaps.
Adding hreflang in the sitemap gives you more flexibility and it’s much easier to manage.
The tool mentioned above will help you generate hreflang tags for the sitemap.
It is technical, but it is essential for international SEO – and can’t be skipped!
4. Choose a URL structure
Selecting the right URL structure is an essential part of international SEO. URL structure defines the layout of your site and how different types of content will be accessible.
There are a few different types of URL structures for international sites:
- ccTLDs
- Subfolders
- Subdomains.
ccTLDs are too expensive and require a lot of management. Subfolders and subdomains are the two best options (as discussed above).
If you’re starting out, using subfolders is the best option as it keeps things clean and you get the best SEO benefits.
Choosing the right URL structure is important for two major reasons (and why you should do your homework and choose the right option keeping in view long-term business growth):
URL structure helps search engines understand your site’s structure to ensure accurate crawling, indexing, and ranking.
It also plays a major role in UX. Some URL structures are more reader-friendly (e.g – ccTLDs) while others aren’t.
Moving from one URL structure to another, at a later stage, is a much bigger hassle. So, make the right decision at the right time.
5. One language, one page rule
You need to use one language per page to improve international optimisation. It keeps the URL structure clean and makes it easier for search engines to serve the most appropriate version to the right audience.
This is what Google recommends:
For example, you can use two different URLs for Canada one each in English and French, and then place all the relevant content and pages within relevant URLs:
- www.yourdomain.com/ca-fr/
- www.yourdomain.com/ca-en/
If you plan to use dynamic or programmatic content (read more about programmatic SEO here) to translate content based on a visitor’s location automatically, it isn’t a good idea from the perspective of international optimisation.
Dynamic content might work for visitors, but it doesn’t work for web crawlers.
It gets easier to manage one page per language when you have a well-defined URL structure for international SEO.
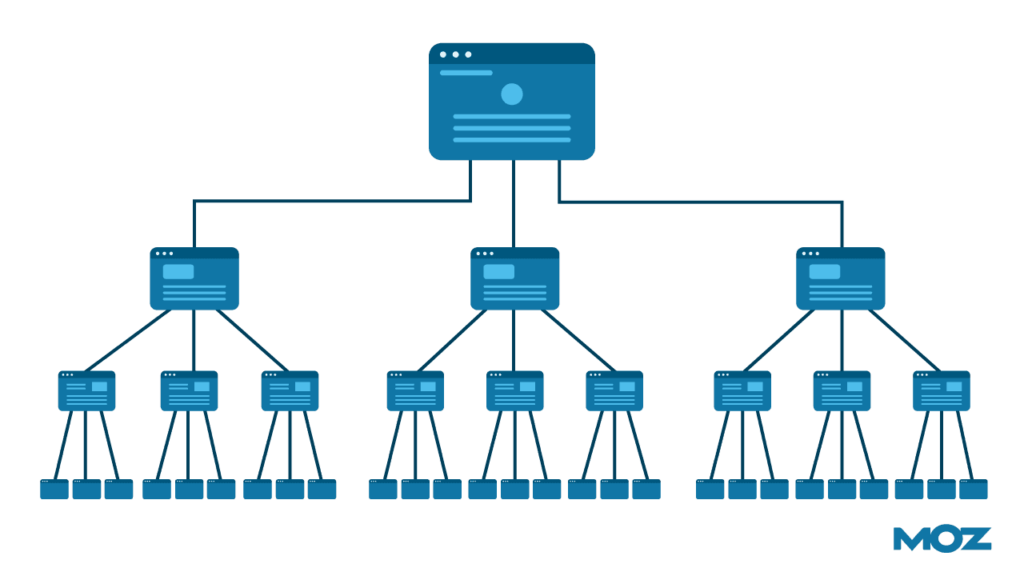
6. Improve internal linking
Linking to the right version and market internally is important for search engines as well as visitors.
Instead of linking randomly, you need to create a layout for each market and have a proper website in the subfolder.
Here’s an example of how to create a clearly defined internal linking structure for each subfolder that targets a separate market:
When you cross-link from one market to another (even if it’s a relevant link), it creates a barrier for crawlers as they fail to make sense of the link.
This means you must enter an international market when you have all the relevant pages and content.
it goes without saying that you shouldn’t create a website for a specific market with incomplete content!
For example, if you have a blog in English and you are planning to enter non-English markets with an intention to link to an English blog from other markets, it won’t work. This needs to be avoided.
Here’s how to manage internal linking for international SEO:
- Clearly define the structure and layout for each market
- Only enter a market when you have everything ready. You’ll end up having thin content if you have a few pages on an international version of your site
- Keep internal links to the same country and/or language
- Maintain a proper website hierarchy
- Regularly monitor internal links via a website audit tool.
7. Build region-specific backlinks
This is where you can benefit from your domain authority if you are using subfolders for international markets.
Some link equity and authority will naturally pass to subfolders, but it isn’t enough.
You need region-specific, relevant backlinks for each market.
If you are using ccTLD, this is where it hurts the most because you start fresh in every market.
For sub-domains, you can’t leverage your main domain’s authority as search engines consider subdomains as separate domains.
Having subfolders for international URL structuring works best as it gives you a jump start right away.
Irrespective of URL structure, regional backlinks are essential. They send relevant signals to search engines leading to better search presence in international markets.
A region-specific backlink is one that you get from the location of your presence. For Mexico, for example, you’ll need links from Mexico-based sites and businesses.
This includes both language-based and location-based links.
Here’s how you can acquire regional backlinks:
- Acquire relevant business profiles such as Google Business Profiles in all the markets
- Use local resources such as business partners, suppliers, agents, etc., and ask them to link to your site
- Analyse your competitor’s backlink profile in each market and see where they are getting their backlinks from. Use it as a benchmark for your outreach campaign
- Leverage geo-specific anchor text
- Find local bloggers and influencers, and reach out to them for collaborations
- Sponsor a local event. This will help you get a few quality local backlinks from the event organiser and its partner sites.
Conclusion
We’re living in an era where personalisation is preferred over everything else.
Around 89% of marketers see a positive ROI when they use personalisation in their marketing campaigns.
International SEO is one way to offer highly personalised content and experience to an international audience.
You could reach your audience in different markets with the same website, but it won’t be personalised regionally.
And your potential customers might switch to your competitor because they have a localised website that communicates to them better.
It all starts with setting a preferred URL structure, setting up hreflang, designing unique landing pages, and entering one market at a time.
If you have any questions about a planned or current international SEO strategy, you can always reach out to one of our senior SEO specialists for assistance.
You can book a strategy call here and see how our team can help you!
Find out how our SEO management services can help your business grow in 2024